2023 IPCC Synthesis Report - Summary for Policymakers
The Synthesis Report of the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) was adopted on March 19, 2023 by 195 governments at Interlaken, Switzerland. It includes a summary for policymakers and a longer report that was released on March 22, 2023.
In the introduction, the IPCC scientists recognize the interdependence of climate, ecosystems and biodiversity, and human societies.
Current Status and Trends
This section opens with the reminder that human activities, principally through emissions of greenhouse gases, have unequivocally caused global warming, with global surface temperature reaching 1.1°C above 1850-1900 in 2011-2020.
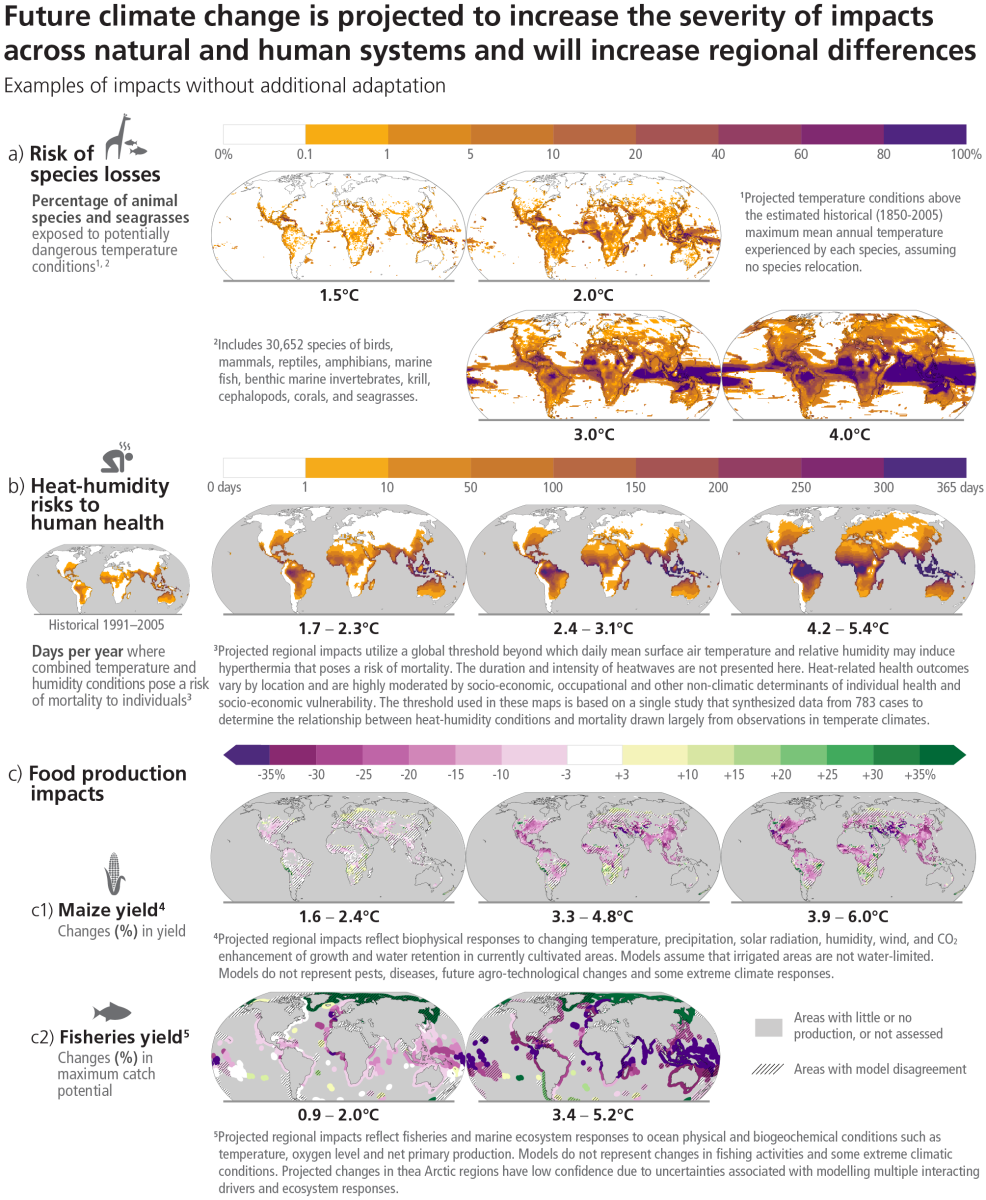
Climate change has caused widespread adverse impacts and related losses and damages to nature and people in every region across the globe. However, vulnerable communities who have historically contributed the least to current climate change are disproportionately affected.
Long-term Climate and Development Futures
The report highlights that global warming will continue to increase in the near term (2021-2040) with the best estimate of reaching 1.5°C in the near term in considered scenarios and modeled pathways.
The likelihood of abrupt and/or irreversible changes increases with higher global warming levels. These risks include species extinction or irreversible loss of biodiversity in ecosystems including forests, coral reefs, and in Arctic regions. Deep, rapid, and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions are part of the solution. solutions exist as a drastic, fast, and sustainable reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The IPCC observes progress in adaptation across all sectors and regions, but it remains insufficient. Maladaptation is happening in some sectors and regions but can be avoided by flexible, multi-sectoral, inclusive, long-term planning and implementation of adaptation actions, with co-benefits to many sectors and systems.
Near-Term Responses in a Changing Climate
Scientists are final: to secure a liveable and sustainable future for all, there is a rapidly closing window of opportunity. Deep, rapid, and sustainable mitigation and accelerated implementation of adaptation actions in this decade would reduce projected losses and damages for humans and ecosystems, while delivering a series of co-benefits, such as biodiversity conservation.